4 Types of Plastic Moulding
In today’s world of manufacturing, plastics are used to make a whole range of products, from automotive body parts to in some cases human body parts. Each moulding process requires a special manufacturing process that moulds the parts based on their specifications. In this article, we will be looking at 4 different types of plastic moulding techniques and their advantages and applications.
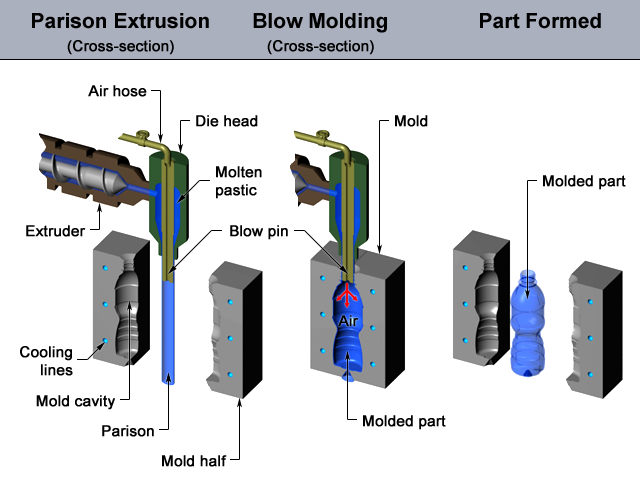
Blow Moulding
This type of moulding is well suited for hollow objects, like bottles. The blowing process follows the basic steps that you would find in glass blowing. A parison, or heated mass of plastic, is placed in a tube and then inflated by air. The air then pushes the plastic against the mould meaning that it takes the form of its desired shape. The plastic is then left to cool, then ejected once it is at its desired temperature.
The blow mould process is perfectly designed to manufacture at high volume for one-piece hollow objects. This moulding process creates uniformed walled containers, perfect if you’re looking to manufacture lots of bottles.
Injection Moulding
This moulding method is well suited for high-quality, high-volume part manufacturing. Plastic injection moulding is seen to be the most versatile of all moulding techniques. The presses that are used in this moulding process vary in size and are rated based on their pressure and tonnage. Large injection machines can create car parts. Whereas, smaller machines can produce very precise parts. During the injection moulding process, there are many types of plastic resins that can help increase its flexibility.
This production process itself is fairly straightforward; however, there are a variety of enhancements and customization techniques that can be used to help produce a unique and desired finish or structure for the product. Injection moulds contain cavities so that when the melted plastic is injected it will fill the cavities and therefore, take the desired shape. Once the plastic is cool, the parts are then ejected using pins.
The initial mould making costs is relatively high; however, the cost per part is very economical. Low part costs along with resin and finish options have all contributed to injection moulding’s popularity in today’s manufacturing industry.
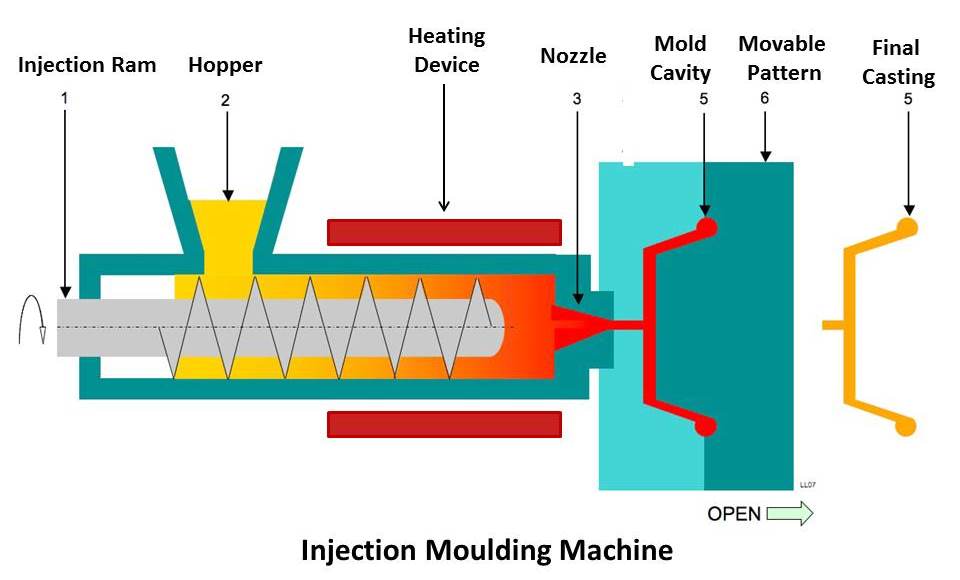
Injection Moulding
Thermoforming
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process where a plastic sheet is heated to a pliable forming temperature, formed to a specific shape in a mold, and trimmed to create a usable product. The sheet, or “film” when referring to thinner gauges and certain material types, is heated in an oven to a high-enough temperature that permits it to be stretched into or onto a mold and cooled to a finished shape. Its simplified version is vacuum forming.
In its simplest form, a small tabletop or lab size machine can be used to heat small cut sections of plastic sheets and stretch them over a mold using a vacuum. This method is often used for sample and prototype parts. In complex and high-volume applications, very large production machines are utilized to heat and form the plastic sheet. And trim the formed parts from the sheet in a continuous high-speed process and can produce many thousands of finished parts per hour depending on the machine and mold size and the size of the parts being formed.
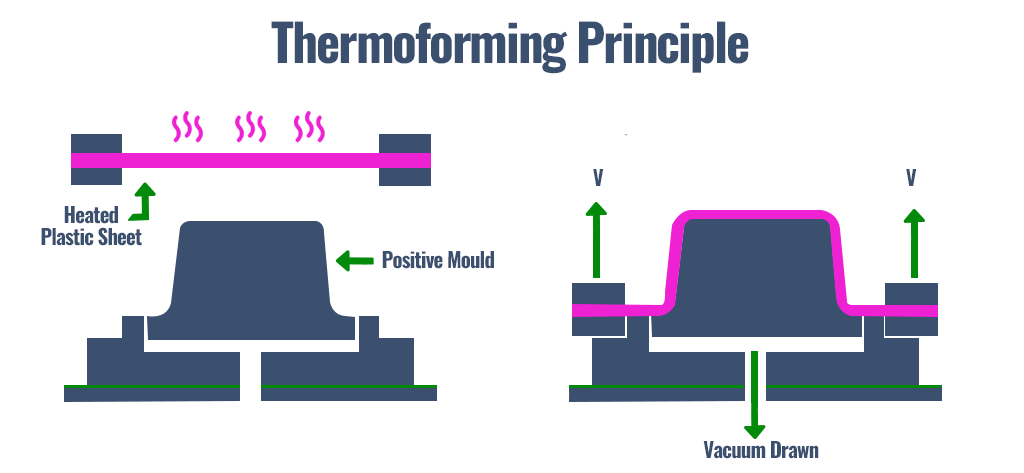
Thermoforming
Compression molding
Compression molding is used with thermosetting plastics. The thermoset plastic material may be in free-flowing granular form or viscous material. The material is placed in a hot mold, and the mold is closed by a hydraulic press. A typical compression molding process is performed at a mold temperature of 350°F and mold pressure of 100 psi (180°C and 700 kPa) with a curing time of 3 min. After the material is cured, the mold is opened and the plastic package is pushed out. Compression molding is a low cost process and is capable of high volume production.
It typically employs a matched metal tool in a heated (normally hydraulic) press to consolidate sheet materials or moulding compounds at relatively high pressures. Examples of composites that are commonly processed by compression moulding include thermosetting prepregs, fibre-reinforced thermoplastic “organ sheets”, moulding compounds. Such as sheet moulding compound (SMC), and chopped thermoplastic tapes. It is also widely used to produce sandwich structures that incorporate a core material. Such as a honeycomb or polymer foam, although care must be taken not to use excessive pressure that might crush the core.
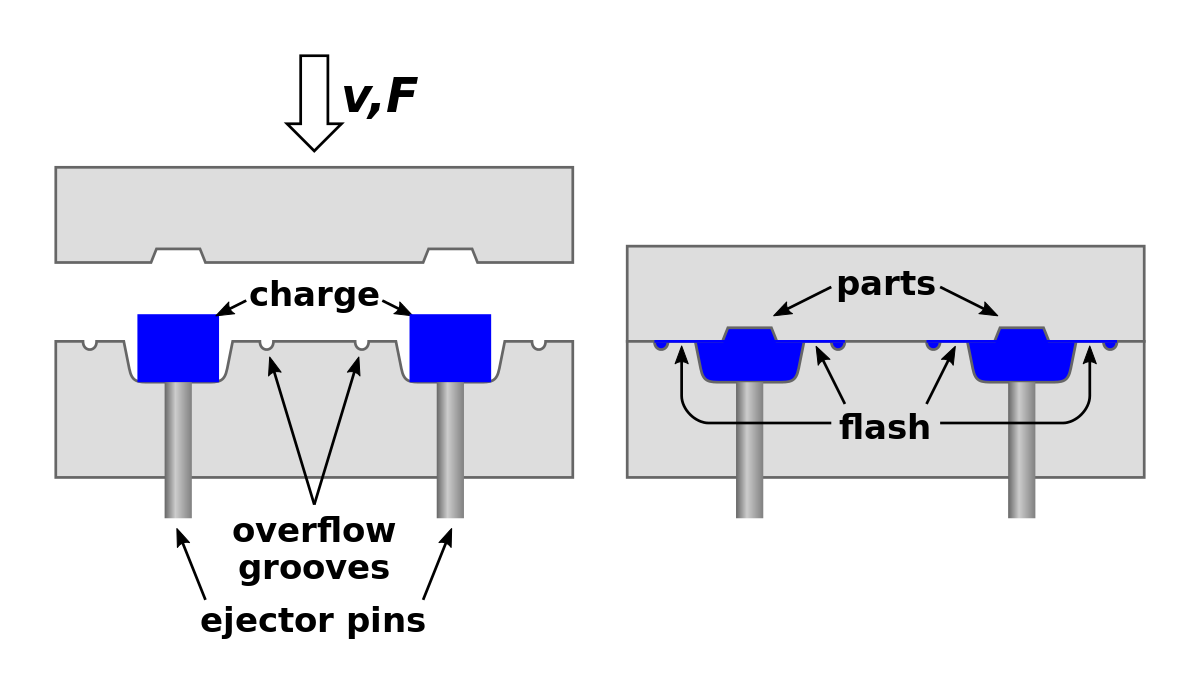
Compression molding






